That is ok. As far as I understand, this is how lemmy<->mastodon activity-pub integration is supposed to work.
Thanks for following us! That's surely a cool feature on the fediverse. Feel welcome and free to post and comment anything related to software engineering.
There is also !seresearch@lemmy.ml which @rahulgopinath@lemmy.ml moderates.
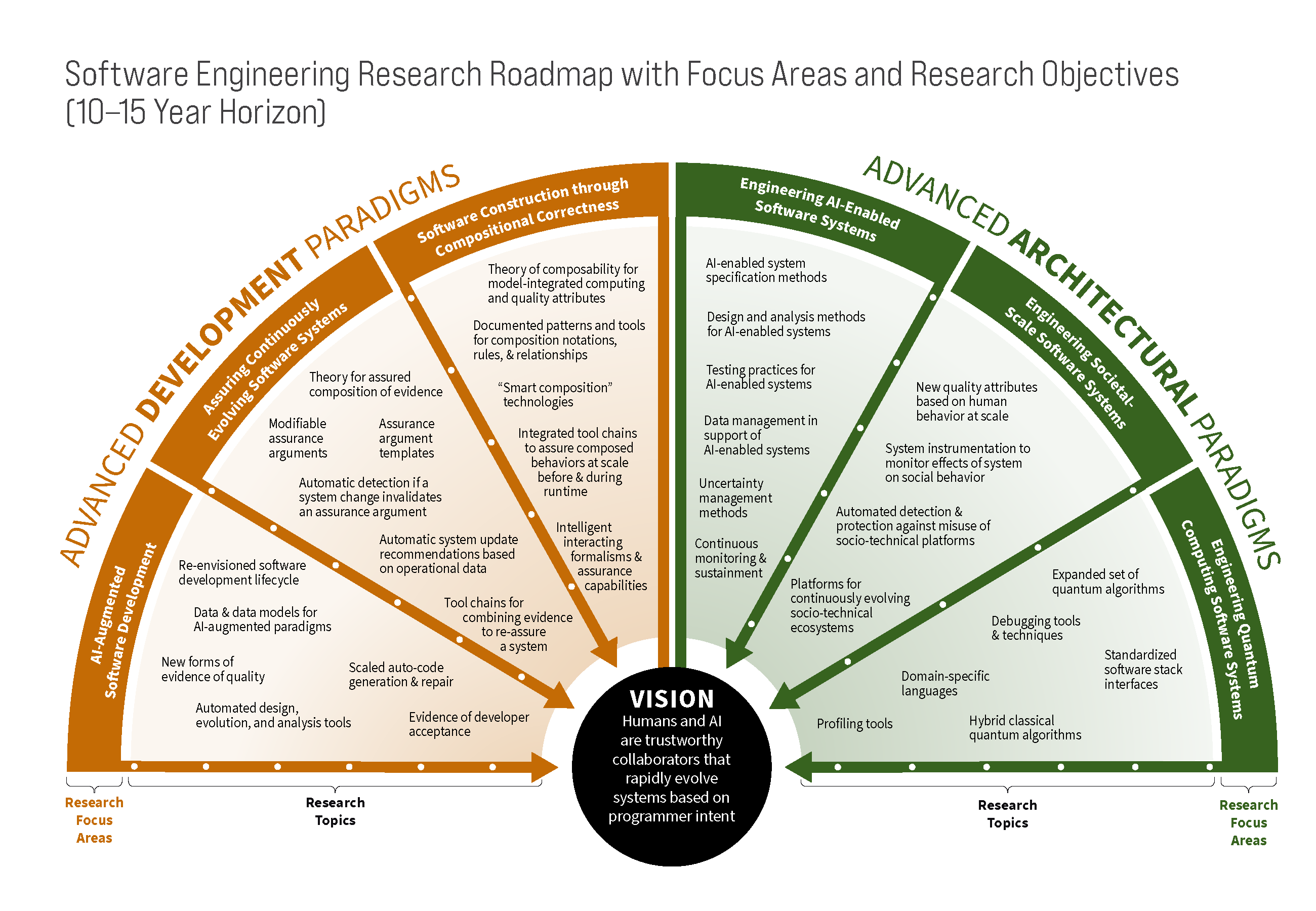
It is almost like the things like PMBOK (which now changed to a principles-based body of knowledge)... these things have no base in scientific method (empirically-based), having origins back to all the DOD needs
Also reminds me of this important research article "The two paradigms of software development research" posted here before https://group.lt/post/46119
The two categories of models use substantially different terminology. The Rational models tend to organize development activities into minor variations of requirements, analysis, design, coding and testing – here called Royce's Taxonomy because of their similarity to the Waterfall Model. All of the Empirical models deviate substantially from Royce's Taxonomy. Royce's Taxonomy – not any particular sequence – has been implicitly co-opted as the dominant software development process theory [5]. That is, many research articles, textbooks and standards assume:
- Virtually all software development activities can be divided into a small number of coherent, loosely-coupled categories.
- The categories are typically the same, regardless of the system under construction, project environment or who is doing the development.
- The categories approximate Royce's Taxonomy. ... Royce's Taxonomy is so ingrained as the dominant paradigm that it may be difficult to imagine a fundamentally different classification. However, good classification systems organize similar instances and help us make useful inferences [98]. Like a good system decomposition, a process model or theory should organize software development activities into categories that have high cohesion (activities within a category are highly related) and loose coupling (activities in different categories are loosely related) [99].
Royce's Taxonomy is a problematic classification because it does not organize like with like. Consider, for example, the design phase. Some design decisions are made by “analysts” during what appears to be “requirements elicitation”, while others are made by “designers” during a “design meeting”, while others are made by “programmers” while “coding” or even “testing.” This means the “design” category exhibits neither high cohesion nor loose coupling. Similarly, consider the “testing” phase. Some kinds of testing are often done by “programmers” during the ostensible “coding” phase (e.g. static code analysis, fixing compilation errors) while others often done by “analysts” during what appears to be “requirements elicitation” (e.g. acceptance testing). Unit testing, meanwhile, includes designing and coding the unit tests.
it’s simply too difficult for average person to login and apply to every single instance that they’re interested in
Maybe there are some misunderstanding, but why would one want to apply to multiple instances at the same time? Just applying and being active on 1 good instance isn't enough?
Totally supportive. Great to have a wayland Rust implementation (and Rust increasing adoption by FOSS community); more specifically, smithay, which further than System76 is building upon, like projects by the community this WM for example https://github.com/MagmaWM/MagmaWM
Wow, this is truly good, as long ago I did read many delays on public healthcare services are due to no-shows. I liked the fact that with the information of who were more likely to no-show, UHP then contacted these people.
UHP was able to cut no-shows for patients who were highly likely to not to show up, by more than half. That patient population went from a dismal 15.63% show rate to a 39.77%. A dramatic increase. At the same time, patients in the moderate category improved from a 42.14% show rate to 50.22%.
Of course, this article sounds like an ad for eClinicalWorks, but interesting and very good application of AI regardless.
For now I mostly see work like these towards the construction phase. Little by little we automate the whole thing.
Just me doing a literature note:
Authors try to find faster algorithms for sorting sequences of 3-5 elements (as programs call them the most for larger sorts) with the computer's assembly instead of higher-level C, with possible instructions' combinations similar to a game of Go 10^700. After the instruction selection for adding to the algorithm, if the test output, given the current selected instructions, is different form the expected output, the model invalidates "the entire algorithm"? This way, ended up with algorithms for the "LLVM libc++ sorting library that were up to 70% faster for shorter sequences and about 1.7% faster for sequences exceeding 250,000 elements." Then they translated the assembly to C++ for LLVM libc++.
A cosmic hydrogen fog??? That sounds like an atmosphere, something that a space-dwelling creature from a sci-fi novel could develop in
not gonna lie, i lol
Well; darwin users, just as linux users, should also work on making packages available to their platforms as Nix is still in its adoption phase. There are many already. IIRC I, who never use MacOS, made some effort into making 1 or 2 packages (likely more) to build on darwin.
as Reddit now going to IPO. That happened to Twitter->Mastodon, can happen to Reddit->Lemmy as well.
We had seen it coming haha
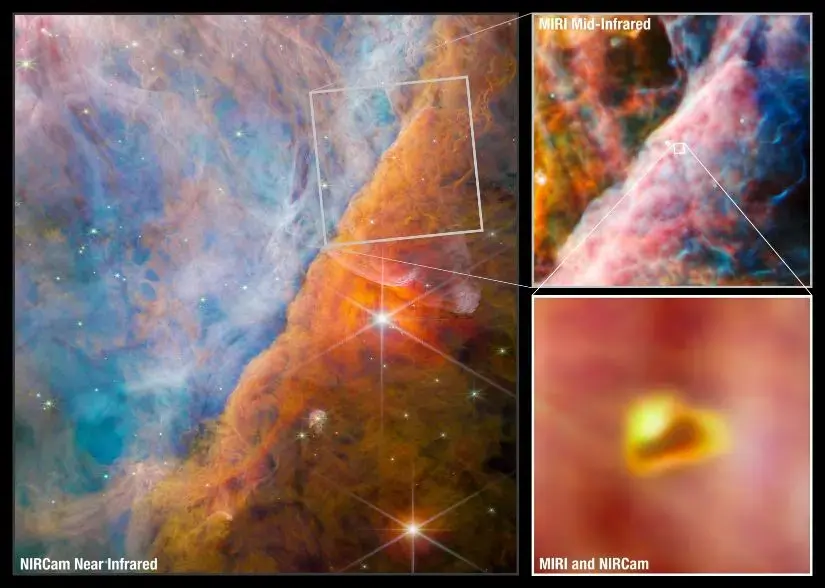

oh this is one of my wallpapers
i did a 1920x1080 version out of it by horizontally tiling 3 duplicates of it like this (i got the freely licensed version from wikimedia commons under https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en)