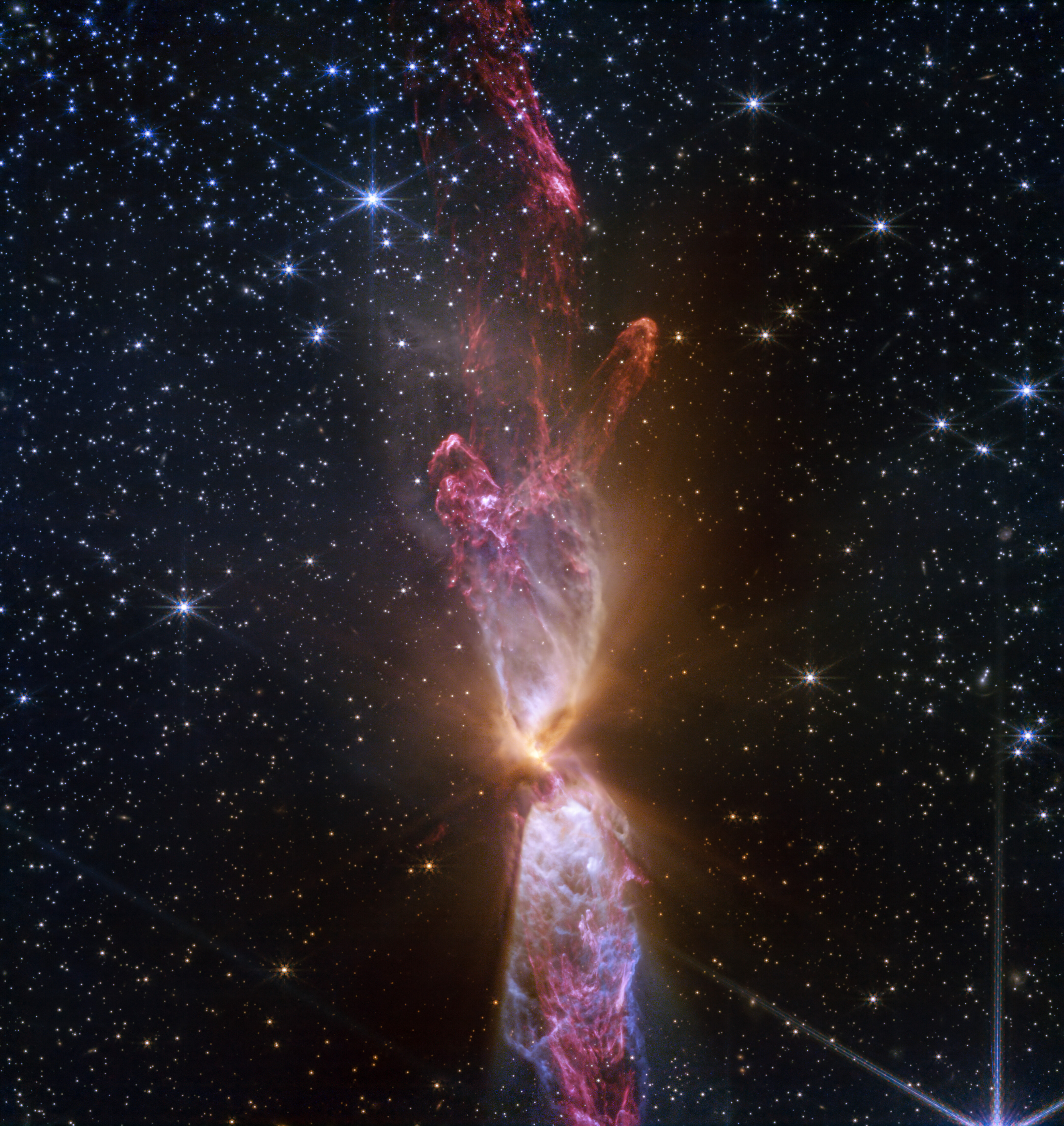
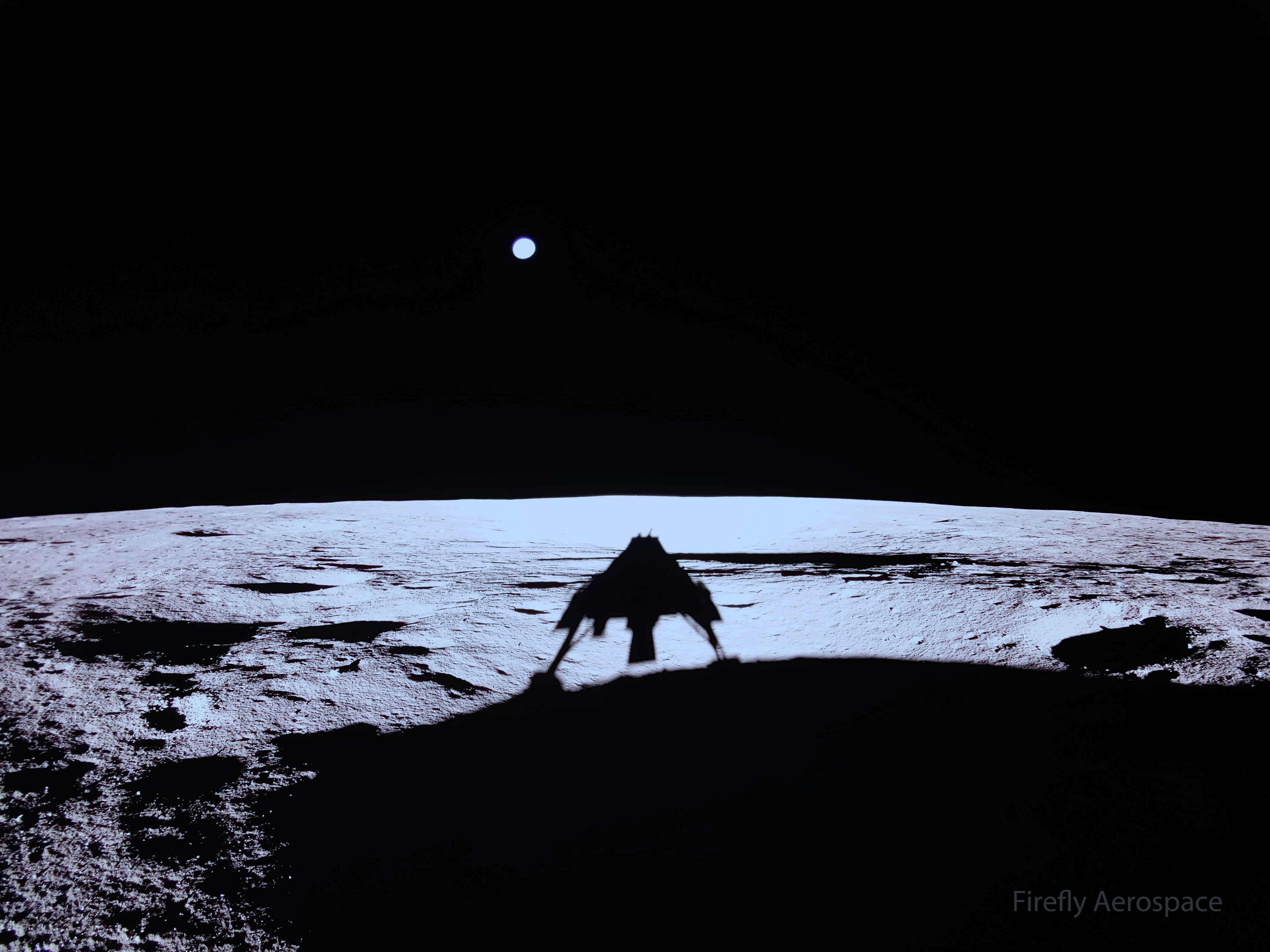
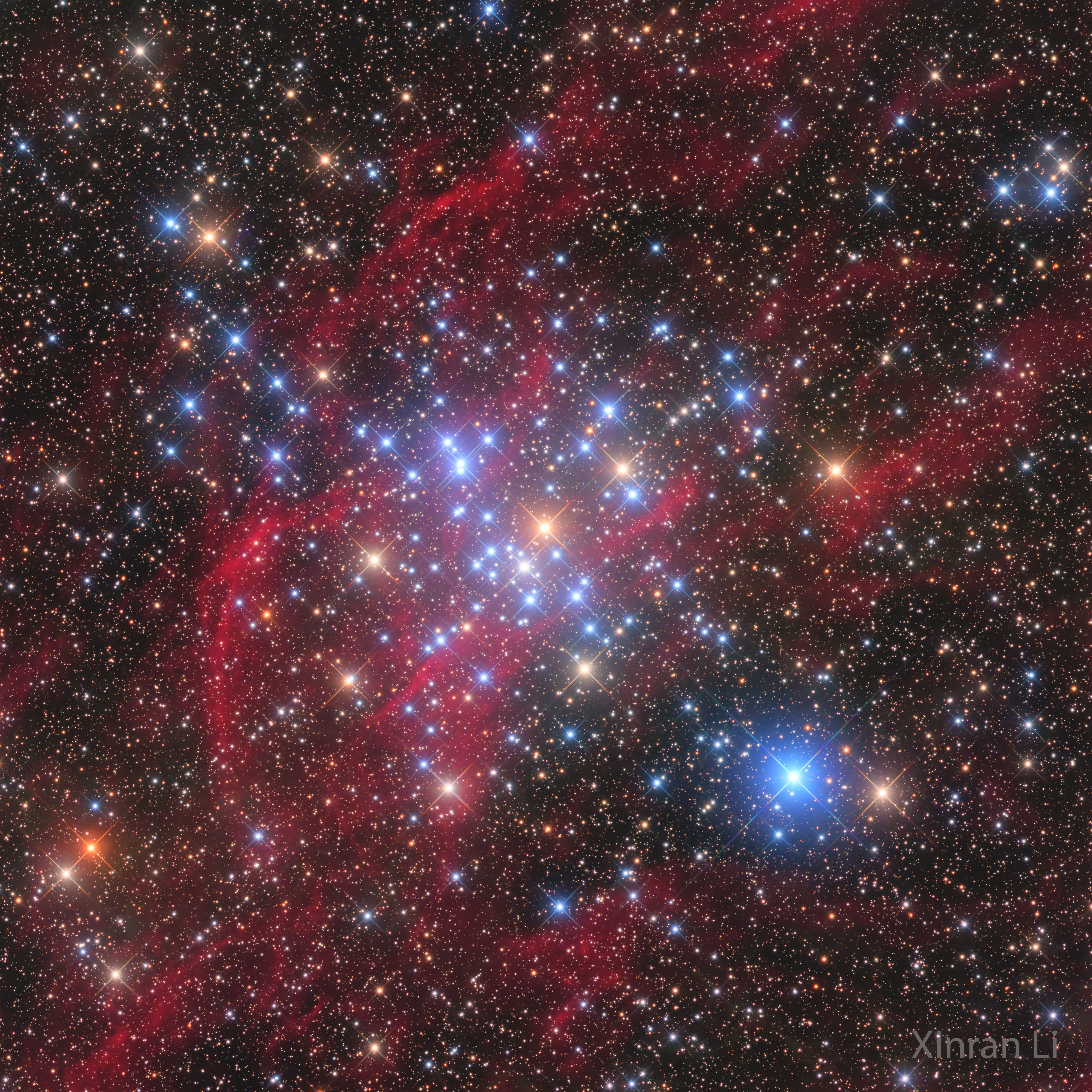
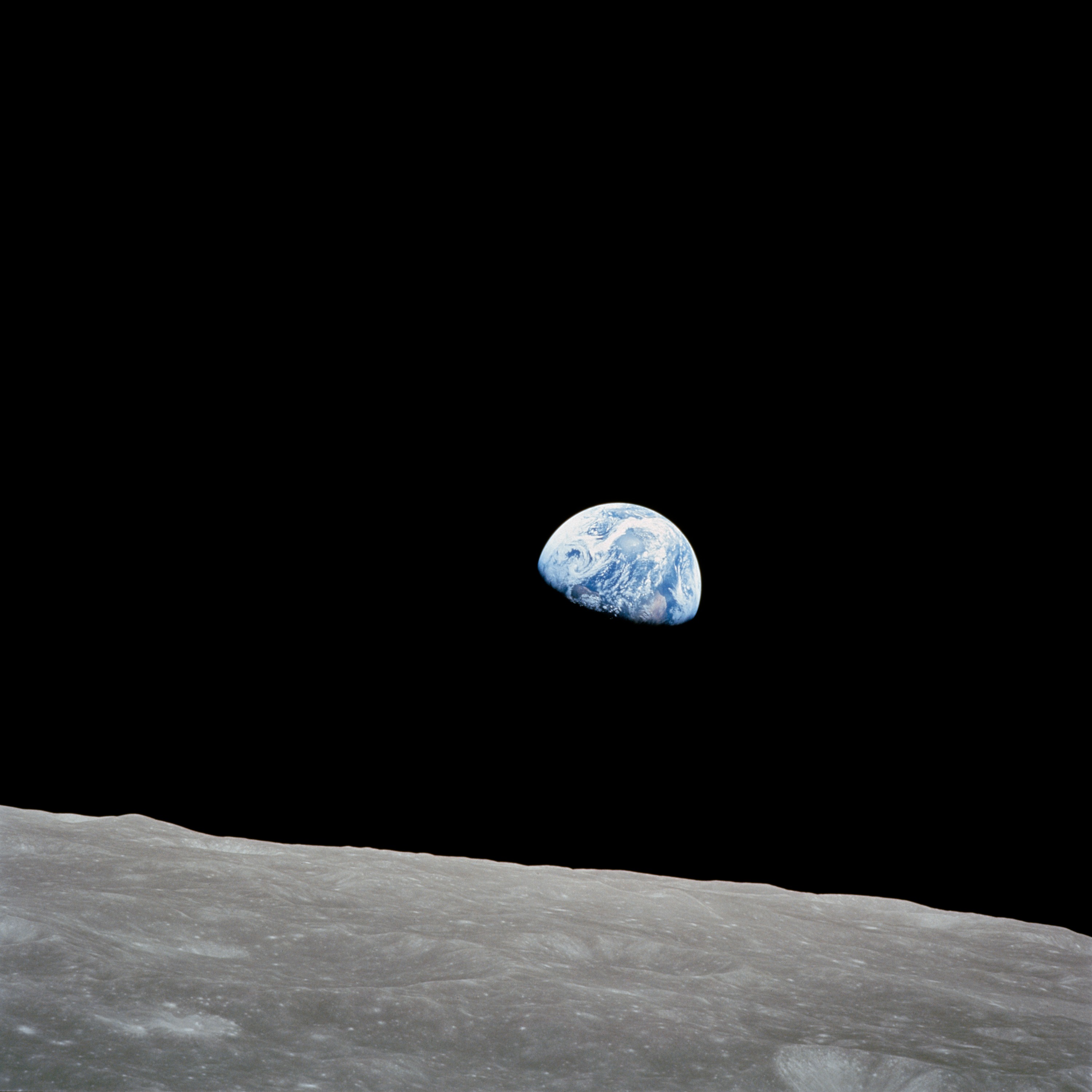
Space
7428 readers
10 users here now
News and findings about our cosmos.
Subcommunity of Science
This community's icon was made by Aaron Schneider, under the CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
founded 3 years ago
MODERATORS
1
2
3
4
5
6
30
SpaceX Has Finally Figured Out Why Starship Exploded, And The Reason Is Utterly Embarrassing
(www.planetearthandbeyond.co)
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
view more: next ›